unify.Dataset class is the best way to manage and create datasets.
Datasets support indexing as well as value-based addition and removal.
unify.log.
The only differences is that datasets each have their own context,
which is automatically managed by the unify.Dataset class.
Uploading
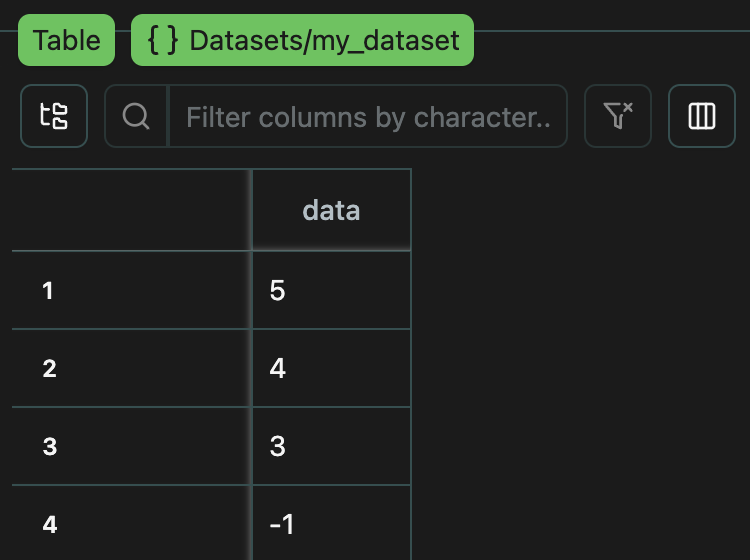
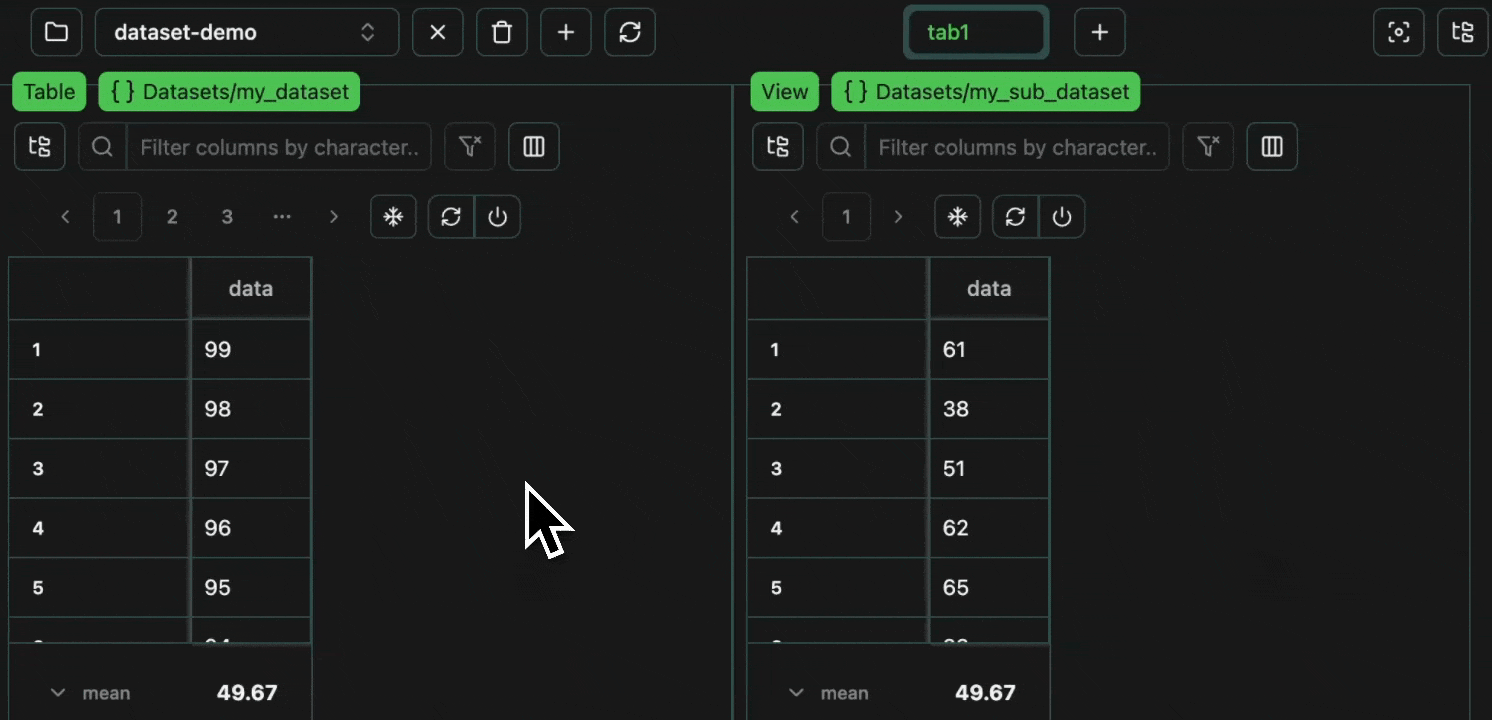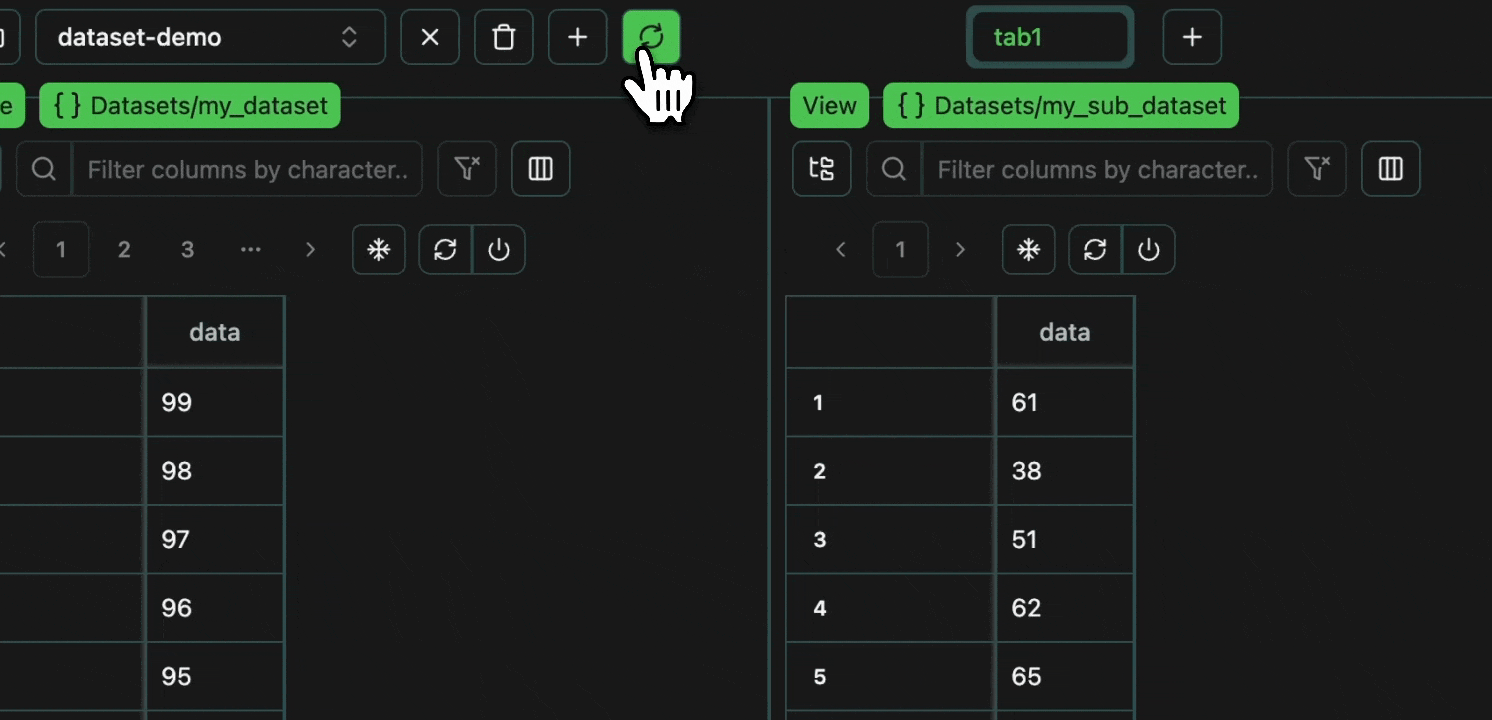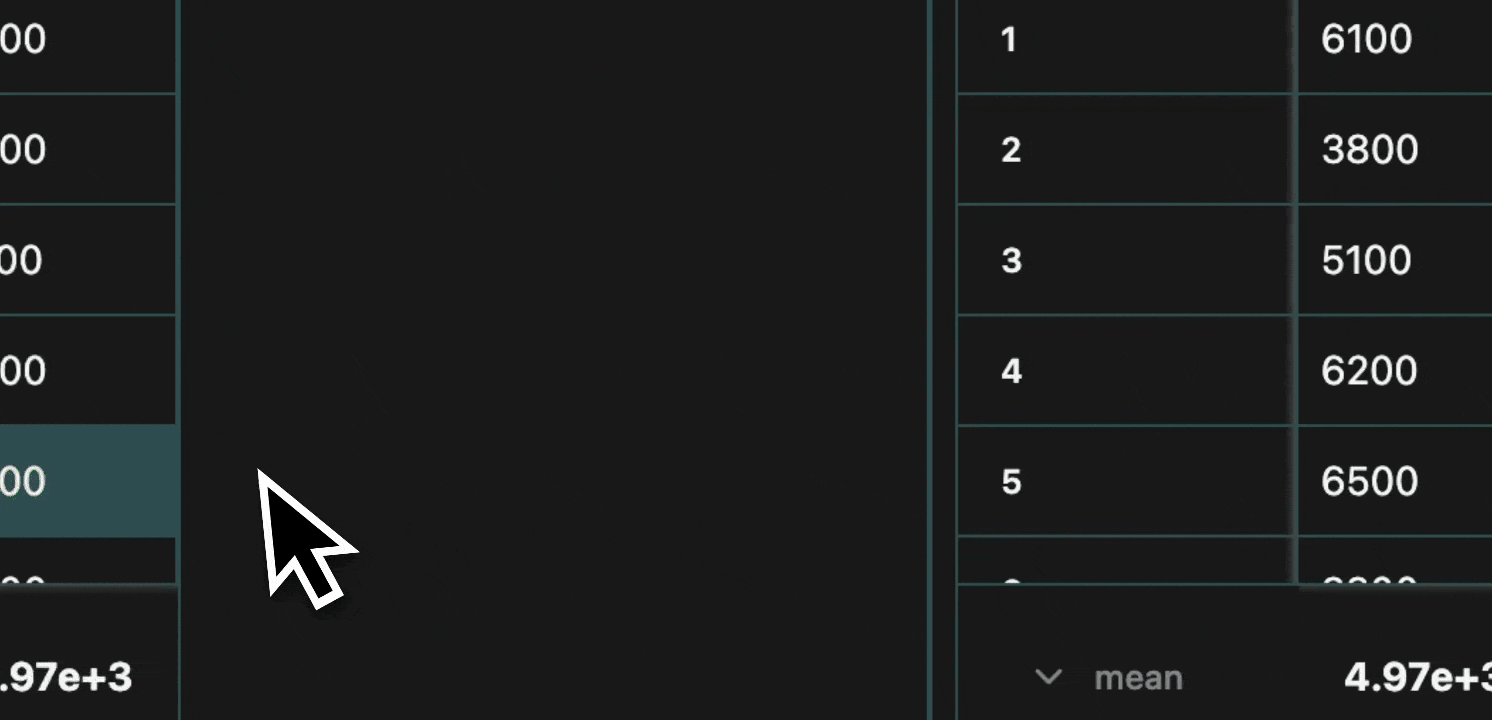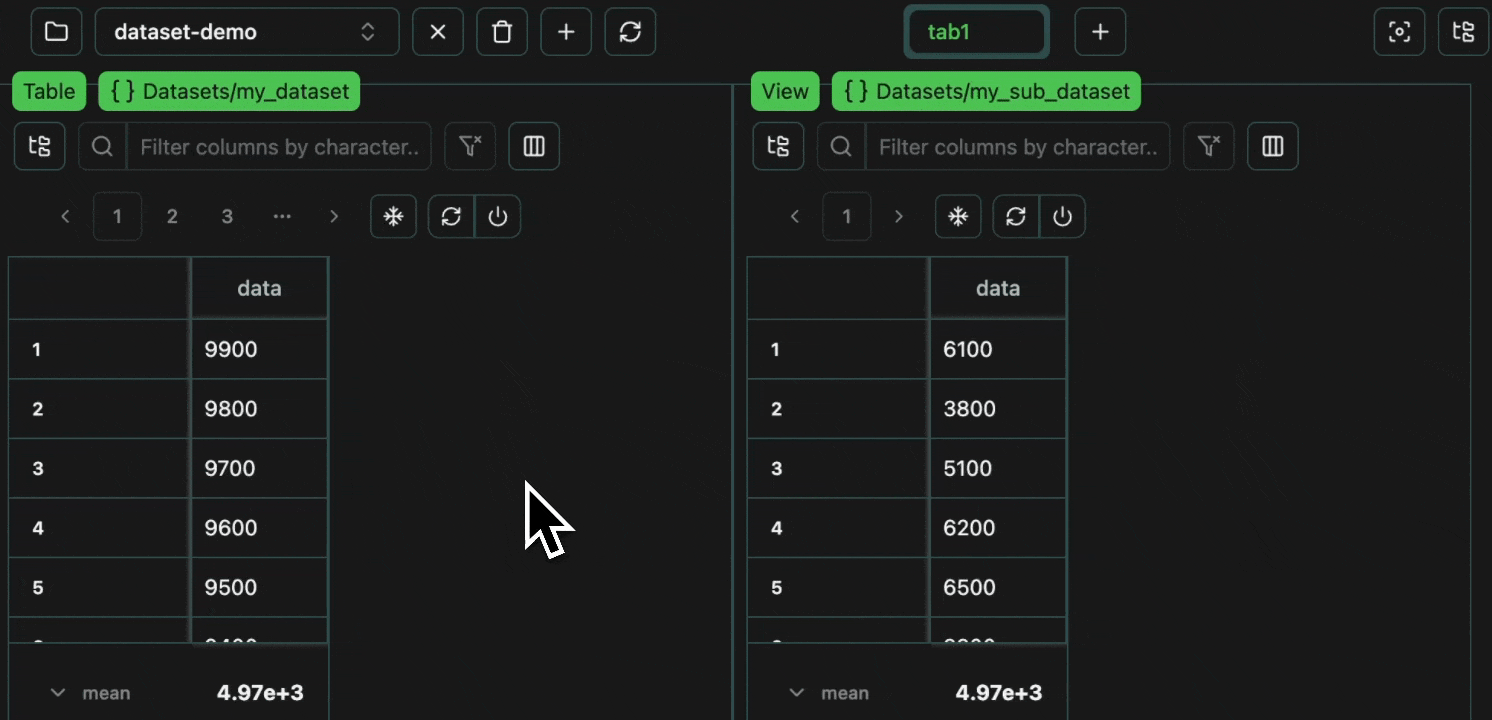
You can upload any dataset to your interface like so.unify.Dataset class automatically sets the context as f"Datasets/{name}",
so your dataset can be viewed at Datasets/my_dataset.
Expand
Expand
 click image to maximize
click image to maximizeoverwrite=True will overwrite any existing dataset with the same name
(even if the upstream dataset contained more data which is not included in the uploaded data).
Downloading
If your dataset already exists upstream, you can download it like so.overwrite=True will overwrite your local dataset
(even if your local dataset contained more data than is present in the download).
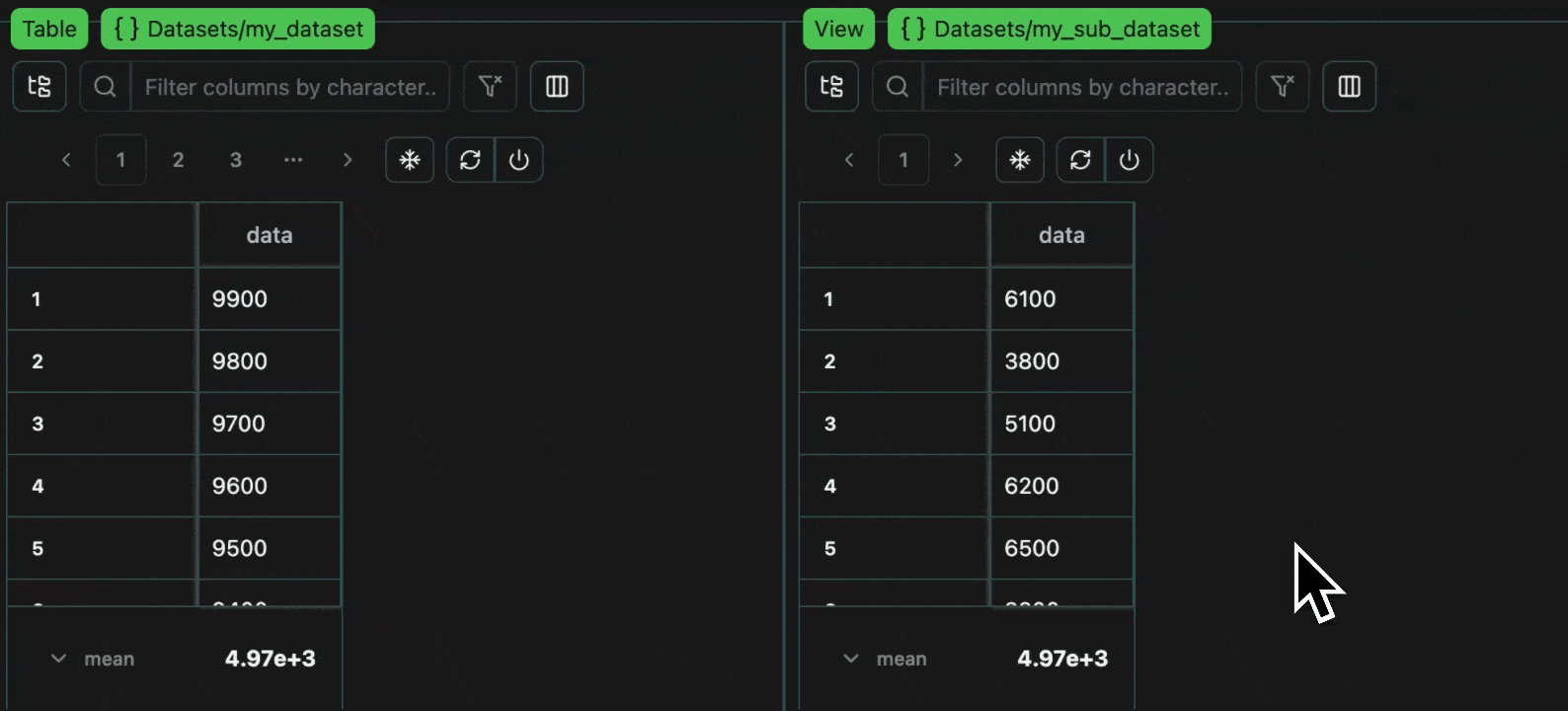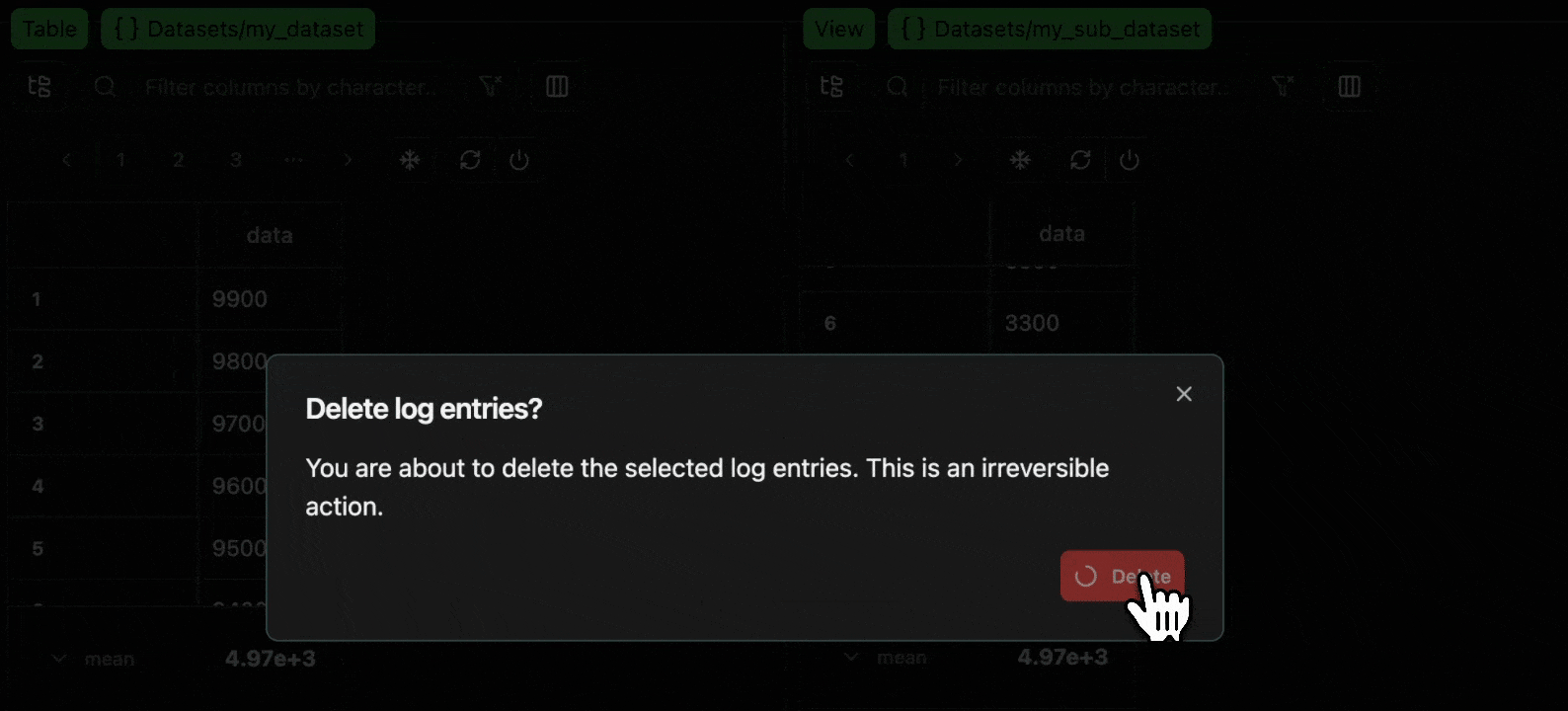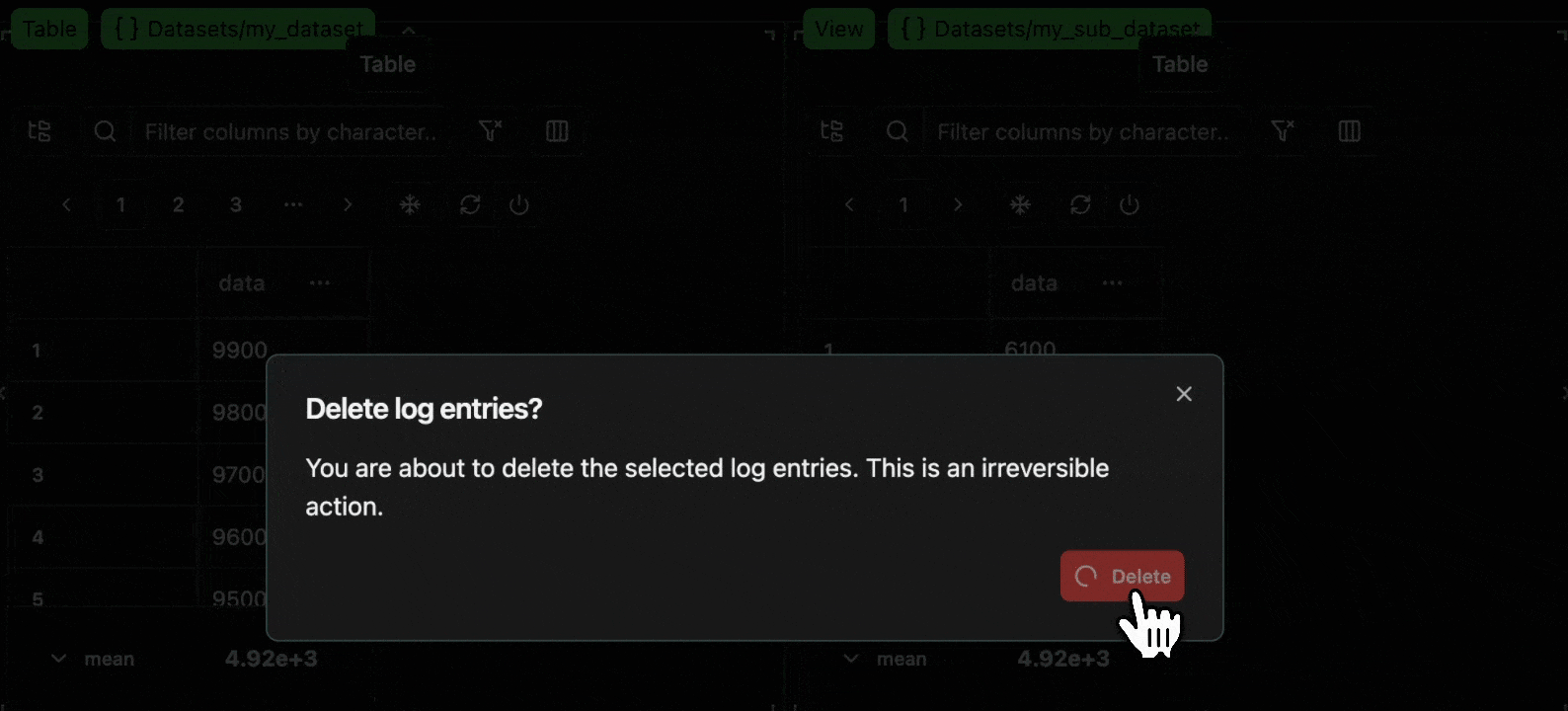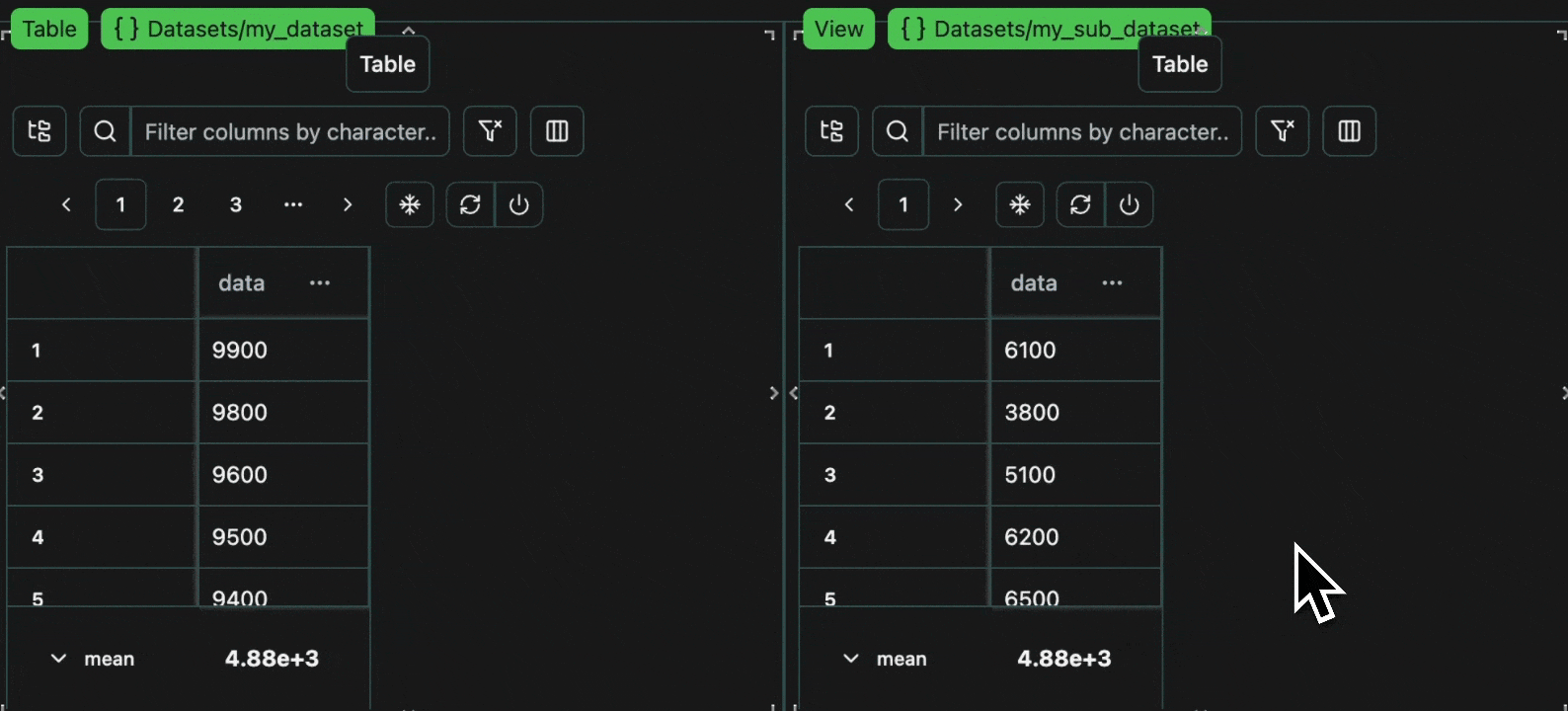
Syncing
Finally, if you want to sync your local dataset with the upstream version, to achieve the superset of the upstream and local data, you can do so like so.overwrite=False to create the superset upstream,
and then downloads with overwrite=True to get this superset dataset downloaded locally,
with every entry now including the unique log ID.
Duplicates
By default, theunify.Dataset class will not allow duplicate values.
allow_duplicates flag when creating the dataset.
allow_duplicates is set to False, then all upstream logs with identical values to local (id-less) logs will be assumed to represent the same log,
and the unset log ids of these local logs will be updated to match the upstream ids with the matching values.
If allow_duplicates is set to True,
then any upstream logs with identical values to local logs will assume to represent different logs unless the log ids match exactly.
If duplicates are not explicitly required for a dataset,
then it’s best to use the default behaviour, and leave allow_duplicates set to False.
Even if duplicates are needed, adding an extra example_id column with allow_duplicates kept as False can be worthwhile to avoid accidental duplication,
especially if you’re regularly syncing datasets between local and upstream sources.
Expand
Expand
 click image to maximize
click image to maximizeExpand
Expand
 click image to maximize
click image to maximizeExpand
Expand
 click image to maximize
click image to maximize